
White eyes in Drosophila melanogaster flies, the first sex-linked gene ever discovered. Calico or tortoiseshell cats, those which have orange-and-black fur. There are few examples of X-linked dominant diseases the best known in this category is vitamin D resistant rickets. A mother with one copy of the gene has a 50% chance of passing it to her children of both sexes, but her daughters will just be carriers of the gene unless their father has it too.ĭiseases well known for their X-linked recessive inheritance are hemophilia (types A and B), and color blindness. He can not pass it to his sons because a male receives his X chromosome from his mother. However, if the disease shows up late in life, or is not severe, he will pass the gene to all of his daughters. Even those males who survive childhood are unlikely to father children because a sickly male will be less likely to find a mate. Sex linkage Sex linkage is the phenotypic expression of an allele that is related to the chromosomal sex of the individual. This is unlikely because severe genetic diseases often cause death in childhood or early adulthood. This is because males, who always have the disease and are not just carriers, would have to father a daughter to pass on the gene. Recessive genes on the X chromosome that cause serious diseases are usually passed from female carriers to their ill sons and carrier daughters. However, they will still be carriers if they receive one copy of the gene. Females must receive a copy of the gene from both parents to have such a recessive disease. X-linked inherited diseases occur far more frequently in males because they only have one X chromosome. 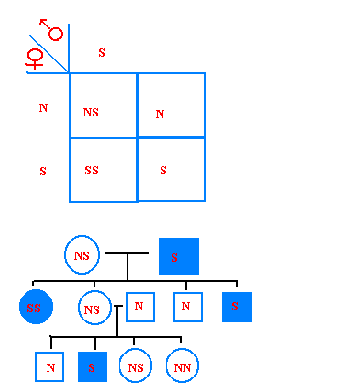
If 1 in 20 males in a human population are green color blind, then 1 in 400 females in the population are expected to be color blind ( 1/ 20)*( 1/ 20). The incidence of recessive X-linked phenotypes in females is the square of that in males (squaring a proportion less than one gives an outcome closer to 0 than the original). In contrast, a female must inherit two mutant alleles, a less frequent event since the mutant allele is rare in the population. Haemophilia is much more common in males than females because males are hemizygous - they only have one copy of the gene in question - and therefore express the trait when they inherit one mutant allele. For example, an X-linked recessive allele in humans causes haemophilia.

X-linked recessive traits are expressed in all heterogametics, but only in those homogametics that are homozygous for the recessive allele. Genes that are present on the X or Y chromosome are called sex linked genes. In mammals, the female is the homogametic sex, having two X chromosomes (XX), while the male is heterogametic, having one X and one Y chromosome (XY). Since, in humans, there are many more genes on the X than there are on the Y, there are many more X-linked traits than there are Y-linked traits. This mode of inheritance is in contrast to the inheritance of traits on autosomal chromosomes, where both sexes have the same probability of expressing the trait. Sex linkage is the phenotypic expression of an allele that is related to the chromosomal sex of the individual.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
